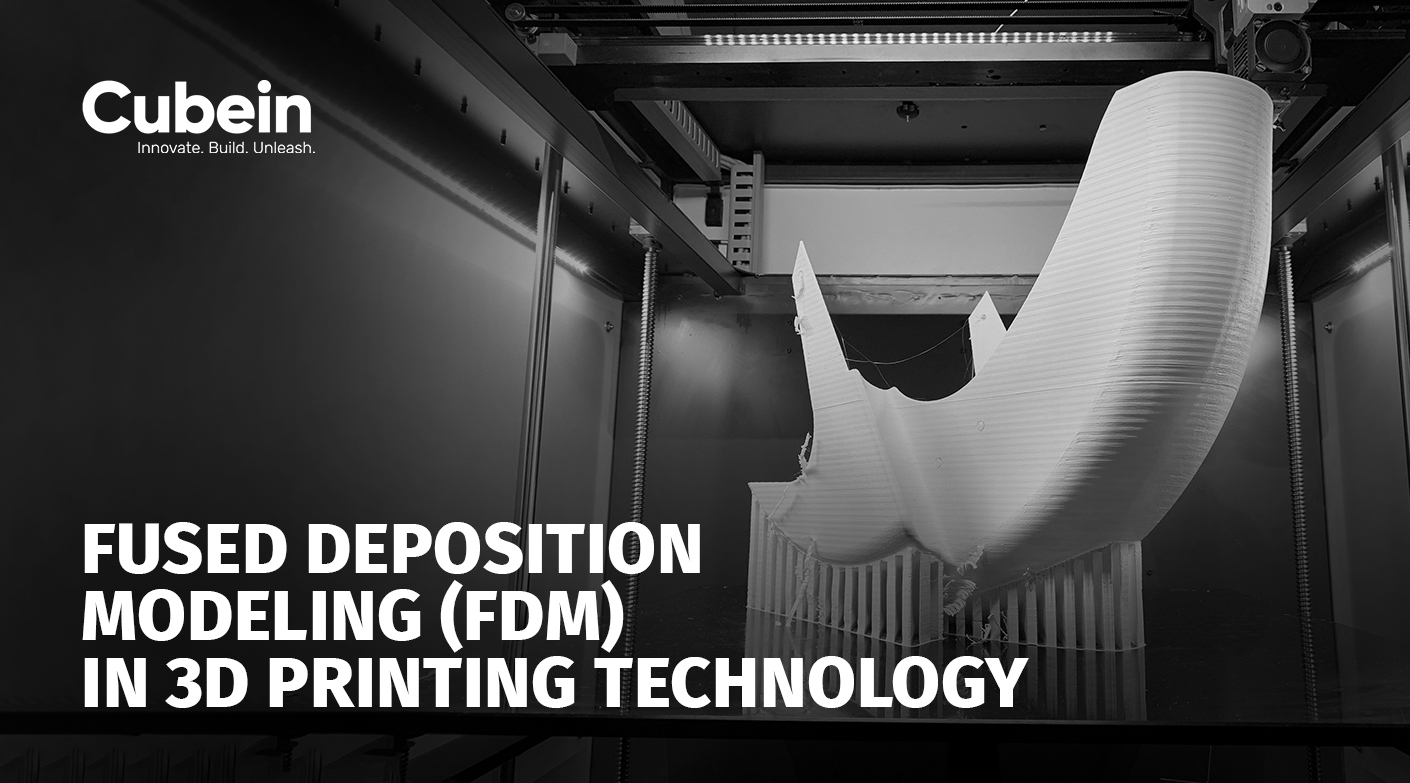
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) has emerged as a revolutionary technology in the world of 3D printing, offering unparalleled versatility and precision. From rapid prototyping to manufacturing functional parts, FDM technology has found widespread applications across various industries.
Whether you’re a professional or a curious enthusiast, understanding the intricacies of FDM 3D printing can unlock a world of possibilities. In this blog, we dive into the fundamentals of Fused Deposition Modeling, exploring its applications, benefits, and future prospects.
What Is Fused Deposition Modeling?
Fused Deposition Modeling, often abbreviated as FDM, stands as one of the most popular methods of 3D printing, cherished for its simplicity and effectiveness. At its core, FDM involves the layer-by-layer deposition of thermoplastic materials to create three-dimensional objects. The process begins with a digital model, which is sliced into thin layers. These layers are then extruded through a heated nozzle and deposited onto a build platform, gradually building up the final object. With its ability to produce complex geometries and functional prototypes, FDM has found widespread adoption across various industries, from manufacturing and aerospace to healthcare and education.
Understanding the Mechanism of FDM 3D printing
In Fused Deposition Modeling 3D printing, the key components include the filament, extruder, heated nozzle, and build platform. The filament, typically made of thermoplastic materials such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) or PLA (Polylactic Acid), serves as the raw material for the printing process. As the filament passes through the extruder, it is heated to its melting point and then extruded through the heated nozzle onto the build platform. The nozzle moves along predefined paths, depositing successive layers of material to gradually form the desired object. The build platform moves vertically or horizontally to accommodate each layer, ensuring precise alignment and dimensional accuracy. Throughout the printing process, precise control of temperature, speed, and layer thickness is essential to achieve optimal results.
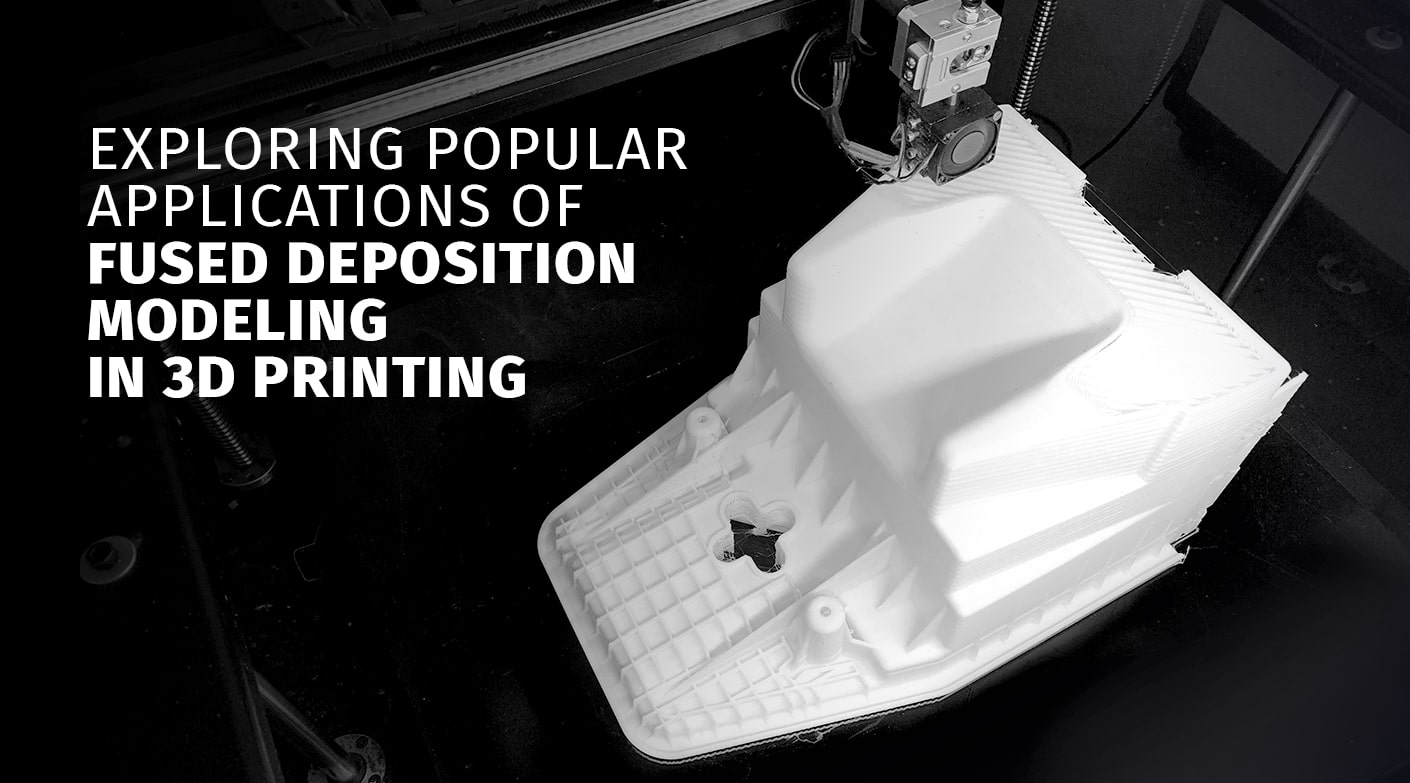
Applications of Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printing
Fused Deposition Modeling 3D printing technology finds diverse applications across various industries:
1. Prototyping:
FDM is widely used for rapid prototyping due to its speed and cost-effectiveness. Engineers and designers can quickly iterate designs and test prototypes before moving into full-scale production.
2. Manufacturing:
FDM technology is increasingly being adopted for manufacturing functional parts, especially in industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. Its ability to produce durable, high-quality parts makes it ideal for end-use production.
3. Education:
FDM 3D printers are commonly used in educational settings to teach students about design, engineering, and manufacturing processes. Students can gain hands-on experience with 3D printing technology, fostering creativity and innovation.
4. Medical:
In the medical field, FDM technology is used for producing patient-specific anatomical models, surgical guides, and prosthetics. Its ability to customize designs and materials makes it invaluable for medical applications.
5. Architecture:
Architects and designers utilize FDM technology to create architectural models and prototypes with intricate details. FDM 3D printing allows for rapid iteration and visualization of design concepts.
Advantages of Fused Deposition Modeling
One of the key advantages of Fused Deposition Modeling is its versatility. FDM printers can accommodate a wide range of thermoplastic materials, including ABS, PLA, PETG, and TPU, offering flexibility in material selection for various applications. Additionally, FDM technology is known for its affordability and ease of use, making it accessible to hobbyists, professionals, and businesses alike.
Disadvantages of Fused Deposition Modeling
While Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) offers numerous advantages, it is not without its limitations and challenges. Understanding these drawbacks is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of FDM 3D printing and mitigating potential issues.
- Limited Resolution and Surface Finish
- Material Limitations
- Structural Weakness
- Support Material Requirements
- Temperature Sensitivity
- Print Speed and Efficiency
- Post-Processing Requirements
Despite these disadvantages, FDM remains a versatile and accessible 3D printing technology, offering unparalleled opportunities for innovation and creativity. By understanding its limitations and implementing best practices, manufacturers, designers, and hobbyists can harness the full potential of FDM 3D printing to realize their visions and drive progress in additive manufacturing.
Importance of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) stands as a pivotal technology in the realm of additive manufacturing, offering a multitude of benefits and driving innovation across industries. Understanding the importance of FDM is crucial for appreciating its role in modern manufacturing and design processes.
- Affordability and Accessibility
- Rapid Prototyping and Iteration
- Customization and Personalization
- Design Freedom and Complexity
- Reduced Material Waste
- On-Demand Manufacturing
- Educational and Research Opportunities
In essence, FDM plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of manufacturing, design, and innovation. Its affordability, versatility, and accessibility democratize the manufacturing process, while its ability to facilitate rapid prototyping, customization, and on-demand manufacturing accelerates innovation and drives progress across industries.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing technology FDM technology has found widespread adoption across diverse industries. Whether it’s rapid prototyping, manufacturing, education, or healthcare, FDM offers unparalleled versatility and efficiency, paving the way for innovation and advancement in the world of 3D printing.
Know more about what is FDM with Cubein, one of India’s leading Advanced ODM service providers, meeting your ideas and innovations.